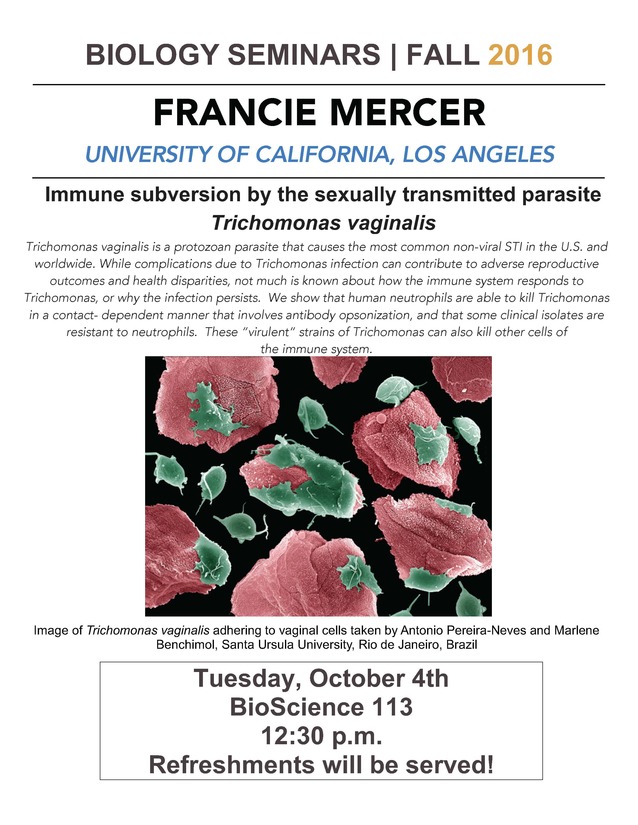
Trichomonas vaginalis is a protozoan parasite that causes the most common non-viral STI in the U.S. and worldwide. While complications due to Trichomonas infection can contribute to adverse reproductive outcomes and health disparities, not much is known about how the immune system responds to Trichomonas, or why the infection persists. We show that human neutrophils are able to kill Trichomonas in a contact- dependent manner that involves antibody opsonization, and that some clinical isolates are resistant to neutrophils. These "virulent" strains of Trichomonas can also kill other cells of the immune system.
